Cognitive Manufacturing: Revolutionizing Production with Mind-Machine Interfaces
The fusion of neurotechnology and industrial processes is ushering in a new era of manufacturing. Cognitive manufacturing, leveraging brain-computer interfaces, promises to redefine how humans interact with machines on the factory floor. This groundbreaking approach enhances precision, boosts productivity, and opens up new possibilities for inclusive workforce participation.
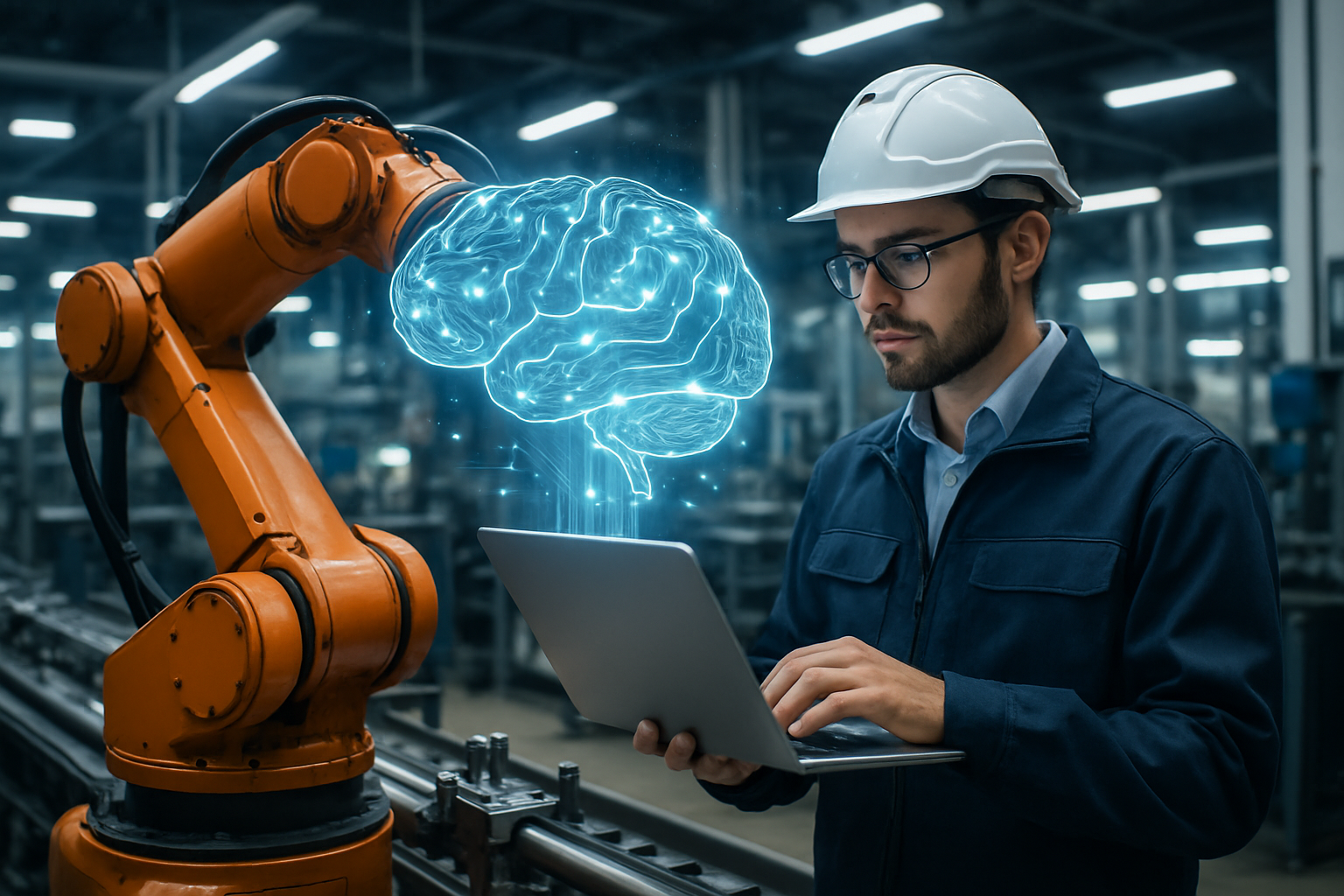

The concept of cognitive manufacturing has its roots in early brain-computer interface research conducted in the 1970s. However, recent advancements in neurotechnology, machine learning, and sensor technology have catapulted this field into practical application. Today, cognitive manufacturing is poised to transform industries ranging from automotive and aerospace to pharmaceuticals and electronics.
How Cognitive Manufacturing Works
At the heart of cognitive manufacturing lies the brain-computer interface, a sophisticated system that translates neural signals into machine commands. These interfaces typically employ electroencephalography (EEG) or other neuroimaging techniques to capture brain activity. Advanced algorithms then interpret these signals, converting them into actionable instructions for manufacturing equipment.
Workers equipped with BCI devices can control robotic arms, adjust production parameters, and even troubleshoot issues simply by thinking about the desired action. This seamless integration of human cognition and machine capability creates a synergy that enhances both precision and efficiency in manufacturing processes.
Benefits and Applications in Industry
The implementation of cognitive manufacturing offers numerous advantages to industrial operations. First and foremost, it dramatically improves precision and reduces error rates. By eliminating the need for physical input devices, workers can execute complex tasks with greater accuracy and speed. This is particularly valuable in industries requiring intricate assembly or precise measurements, such as electronics manufacturing or medical device production.
Cognitive manufacturing also enhances worker safety by reducing physical strain and minimizing exposure to hazardous environments. Operators can control machinery from a safe distance, reducing the risk of accidents and injuries. Additionally, this technology opens up new opportunities for individuals with physical disabilities to participate fully in manufacturing roles, promoting workplace inclusivity and diversity.
Challenges and Considerations
While the potential of cognitive manufacturing is immense, several challenges must be addressed for widespread adoption. One primary concern is the need for extensive training and adaptation periods for workers to become proficient with BCI technology. Companies must invest in comprehensive training programs and be prepared for initial productivity dips as employees acclimate to the new system.
Privacy and security considerations also loom large in the realm of cognitive manufacturing. As BCIs collect and interpret neural data, robust safeguards must be in place to protect worker privacy and prevent unauthorized access to sensitive information. Industry leaders and policymakers must work together to establish clear guidelines and regulations governing the use of neurotechnology in industrial settings.
Future Prospects and Industry Impact
As cognitive manufacturing technology continues to evolve, its impact on the industrial landscape is expected to be profound. Experts predict that by 2030, up to 30% of manufacturing tasks could be performed using brain-computer interfaces, leading to significant gains in productivity and quality control. This shift will likely reshape workforce dynamics, creating new job categories focused on BCI operation and maintenance while potentially displacing certain traditional roles.
The integration of cognitive manufacturing with other emerging technologies, such as artificial intelligence and the Internet of Things, holds immense promise for creating truly intelligent factories. These smart manufacturing ecosystems will be capable of real-time optimization, predictive maintenance, and unprecedented levels of customization, driving innovation across industries.
Maximizing the Potential of Cognitive Manufacturing
-
Invest in comprehensive BCI training programs for employees
-
Collaborate with neurotechnology experts to customize BCI systems for specific industrial applications
-
Implement robust data security measures to protect neural information
-
Develop clear protocols for BCI use in various manufacturing scenarios
-
Regularly assess and update cognitive manufacturing systems to leverage the latest advancements
As cognitive manufacturing continues to evolve, it stands poised to redefine the relationship between human workers and machines in industrial settings. By harnessing the power of thought, this revolutionary approach promises to unlock new levels of precision, efficiency, and innovation in manufacturing processes. As industries adapt to this cognitive revolution, they will not only transform their operations but also open up new frontiers of human potential in the world of production.