Dolphin-Assisted Therapy: A Splash of Controversy in Animal-Human Healing
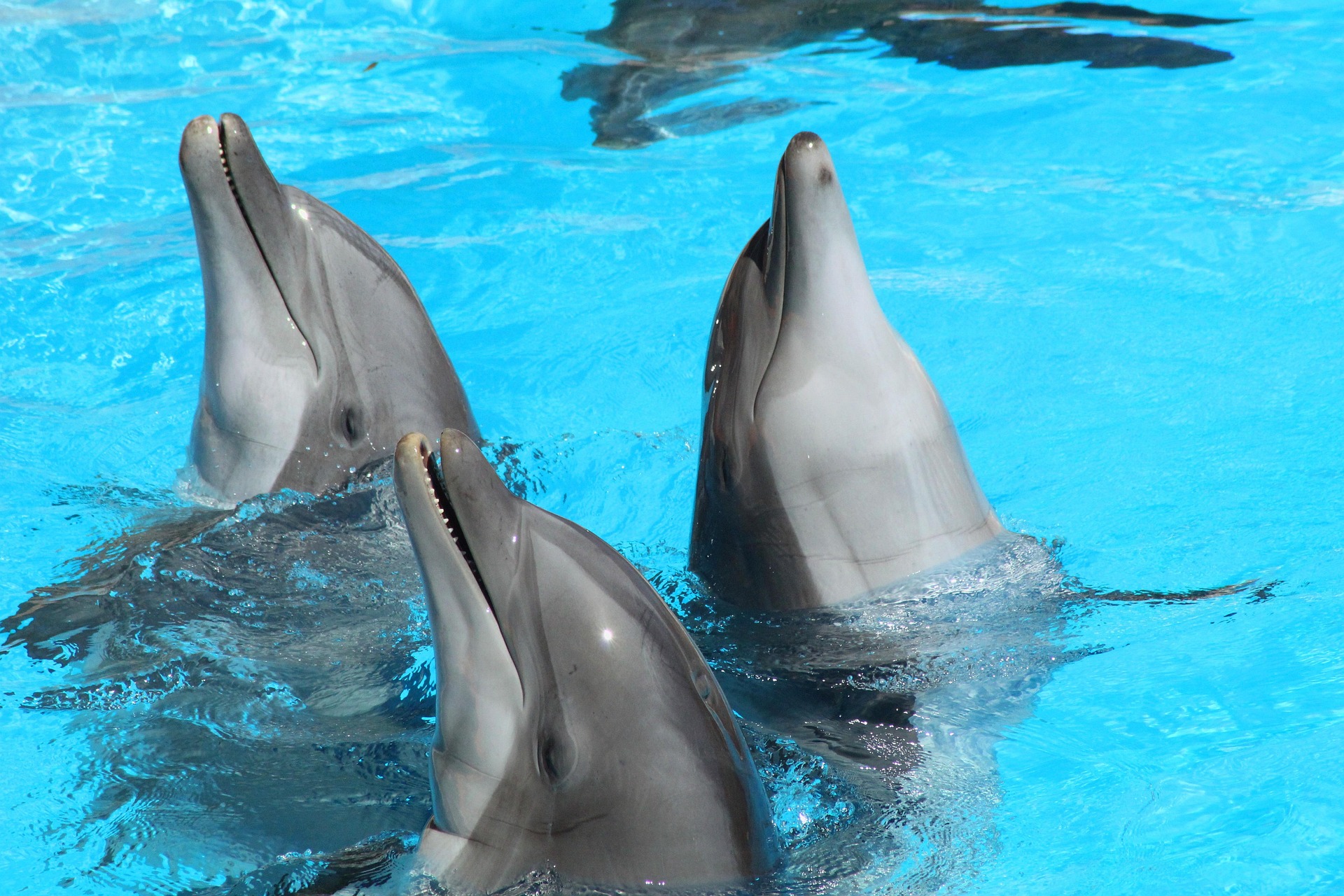
In the realm of alternative therapies, one controversial practice has made waves for decades: dolphin-assisted therapy. This unique approach to healing combines human interaction with these intelligent marine mammals in hopes of addressing various physical and mental health conditions. As the practice gains attention, it also sparks debate among animal welfare advocates, medical professionals, and those seeking alternative treatments.
The Origins of Dolphin-Assisted Therapy
The concept of dolphin-assisted therapy can be traced back to the 1970s when researchers began exploring the potential therapeutic benefits of human-dolphin interactions. Dr. Betsy Smith, a pioneering anthropologist, initiated some of the earliest studies in this field. Her work with children with disabilities suggested that dolphin encounters could lead to improved communication and motor skills.
As word spread about the potential benefits, specialized centers began to emerge in various parts of the world, particularly in coastal areas with access to dolphin populations. These facilities offered programs where individuals could swim with dolphins under supervised conditions, with the belief that such interactions could have positive effects on physical and mental well-being.
The Proposed Benefits and Mechanisms
Advocates of dolphin-assisted therapy claim a wide range of potential benefits for participants. These purported advantages include reduced anxiety and depression, improved motor function in individuals with physical disabilities, enhanced communication skills for those with autism spectrum disorders, and even pain relief for individuals with chronic conditions.
The proposed mechanisms behind these benefits are varied and often debated. Some theories suggest that the calming presence of dolphins and the unique sensory experience of being in water with them can reduce stress and promote relaxation. Others point to the dolphins’ use of echolocation, proposing that the high-frequency sounds emitted by dolphins might have a positive effect on human brain activity.
Scientific Scrutiny and Skepticism
Despite anecdotal reports of success, the scientific community has approached dolphin-assisted therapy with considerable skepticism. Numerous studies have attempted to evaluate the efficacy of DAT, but many have been criticized for methodological flaws, small sample sizes, and lack of proper controls.
A comprehensive review published in the journal Anthrozoös in 2007 examined the available research on dolphin-assisted therapy and concluded that there was no reliable scientific evidence to support its use as a treatment for any condition. Critics argue that any perceived benefits may be due to the placebo effect or simply the result of being in a novel, enjoyable environment rather than any specific influence of the dolphins themselves.
Ethical Concerns and Animal Welfare
One of the most significant controversies surrounding dolphin-assisted therapy relates to the ethical treatment of the animals involved. Animal welfare organizations have raised concerns about the impact of captivity on dolphins, which are highly intelligent and social creatures adapted to life in the open ocean.
Critics argue that confining dolphins to small pools or enclosed areas for therapy sessions can lead to stress, behavioral issues, and compromised health. There are also concerns about the potential for disease transmission between humans and dolphins, as well as the risk of injury to both parties during interactions.
Regulatory Landscape and Industry Practices
The regulation of dolphin-assisted therapy facilities varies widely around the world. In some countries, strict guidelines govern the operation of such programs, while in others, oversight may be limited or non-existent. This lack of consistent regulation has led to concerns about the quality and safety of some DAT programs.
In the United States, the Marine Mammal Protection Act places restrictions on the capture and use of wild dolphins for therapy or entertainment purposes. However, facilities that use captive-bred dolphins or those already in human care may still operate under certain conditions. The debate continues over whether any form of dolphin-assisted therapy can be conducted ethically and without compromising animal welfare.
The Future of Dolphin-Assisted Therapy
As research in the field of animal-assisted therapy continues to evolve, the future of dolphin-assisted therapy remains uncertain. Some proponents are exploring ways to conduct DAT programs in more natural settings, such as protected bays or lagoons, to address concerns about captivity. Others are investigating the use of virtual reality technologies to simulate dolphin interactions, potentially offering a more ethical alternative.
Meanwhile, the scientific community continues to call for more rigorous, well-designed studies to evaluate the efficacy of dolphin-assisted therapy. As our understanding of animal cognition and welfare improves, it is likely that the practices and regulations surrounding DAT will continue to evolve.
In conclusion, dolphin-assisted therapy represents a complex and contentious area at the intersection of alternative medicine, animal welfare, and human-animal interaction. While the allure of healing through connection with these charismatic marine mammals remains strong for many, the practice continues to face significant challenges in terms of scientific validation and ethical considerations. As research progresses and societal attitudes toward animal welfare evolve, the future of dolphin-assisted therapy will likely depend on finding a balance between human therapeutic needs and the well-being of the animals involved.